As a citizen of a nation, we are bound by some duties and liabilities among which tax is one of them. Tax is a compulsory contribution to the government from our end and is something that is levied to you on behalf of the facilities provided by the government. The purview of taxation is pretty wide and there are different ambits to it.
The word tax often brings different queries among us. For say, whether a certain income will be liable to taxation or not, whether our investments need to be taxed or not. It’s a reason why the word taxation is one of the widely discussed matters in our nation.
India currently has the Income Tax Act, 1961 governing the direct taxation rules when it comes to income of a person while other indirect aspects are covered in other acts. For most of us, the income derived from salary, rents, profession or other sources are a known terminology. But when it comes to income from sale and purchase of shares, that’s something people are still unclear about. Let’s find out whether or not you will have to pay the tax on your stock investments down below:
Capital Gains/ Losses on Sale of Stock Investments
Before dwelling deep into the tax on stock investments first we need to take a look at the capital gain or loss aspect. As per the rules of Income Tax, shares are classified as capital assets and hence come under the purview of capital gain. If the share listed on a stock exchange is sold within 12 months of the date of holding, then they are deemed as short term capital assets while those which are held for over 12 months are called long term capital assets.
Here’s a snippet of it:
| Period of Holding | Short term or Long term |
| Less than 12 months | Short Term Capital Asset |
| More than 12 months | Long Term Capital Asset |
Short Term Capital Gains/Losses
If the person holds equity shares or stocks for less than 12 months and sells it then it will culminate in short-term capital gain or loss. Here’s how it can be calculated:
Short-term Capital Gain/Loss: Sale Price = Expenses occurred on Sale – Purchase Price
If the sale price is higher than the purchase price and expenses occurred on sale then short term capital gain will arise and if the same is lower then short term capital loss will arise. Income tax allows you to set off the short term capital loss from the short term or long term capital gain. If the amount is not set off, then it can be carried forward to 8 years and can be adjusted with short term or long term capital gains in these next 8 years.
Tax on Short Term Capital Gain
Short term capital gains are taxed at 15% as per the Income Tax Rules. The rate is irrespective of your tax slab. However, if your total income is below the threshold of the basic slab, i.e. 2.5 lakhs then you can adjust your short term capital gains to fulfil that limit and the rest will be liable to 15% of taxation.
Long Term Capital Gains/ Losses
As we aforementioned above, if a person holds the share over 12 months then the same will incur long term capital gain on the sale.
Here’s how it can be calculated
Long-term Capital Gain/Loss = Sale Price – Cost of Acquisition
Previously when the long term capital asset was exempt from taxation, the losses were not allowed to be set off. But with the amendment of rules, the long term capital losses can now be set off against other long term capital gains and if the same is not completely set off, then it can be carried forward for up to 8 years.
Tax on Long Term Capital Gain
Previously there was no taxation on the long term capital gain made from the sale of equity shares. However, the rules have changed and now if a seller generates more than 1 lakhs on sale of stocks, then that shall attract taxation of 10%. Furthermore, the seller will not be able to avail of the benefits of indexation.
View Source: https://resource.cdn.icai.org/56467bos45796cp4u4.pdf
Securities Transaction Tax (STT) on Sale of Stock
STT is a tax liability that is applicable to the shares that are bought or sold via a stock exchange. Any shares that are listed on the stock exchange shall attract STT on the sale or purchase of it.
What’s ITR?
ITR refers to Income Tax Return which means a form in which the assessee the information regarding his income and taxation liability to the government. There are 7 different ITR forms and an assessee can file the return in the designated form as defined by the Income Tax Act. An assessee showcases all his incomes and expenses derived within the assessment year in the ITR. He/she shall submit the ITR form by 31st July (unless an extended date is offered by Income Tax Dept.). We’ll look at the steps to file the ITR down below.
Steps to File an Income Tax Return
If you earn an income that comes under the ambit of Income Tax Act, 1961 and the same is taxable then you have to file the income tax return showcasing your income. There are different types of ITR forms available based on the type of assessee and we have thoroughly illustrated the same above. You can select the ITR form based on your taxability and file the same. In case, if you fall under ITR 1 and ITR4 you can file the same online. For the rest of the ITR forms, you will have to download the ITR form upload the XML file of the same.
We here look at the step by step procedure for filing the income tax return down below.
Step – 01 Visit the Income Tax Portal: Visit the website www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in
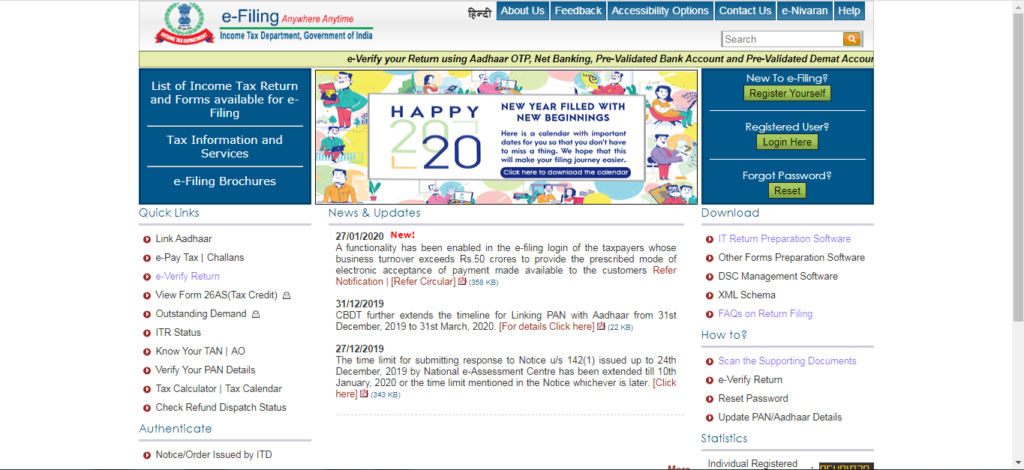
Step – 02 Download ITR Utility Form: Click on the IT Return Preparation Software option placed on the right side.
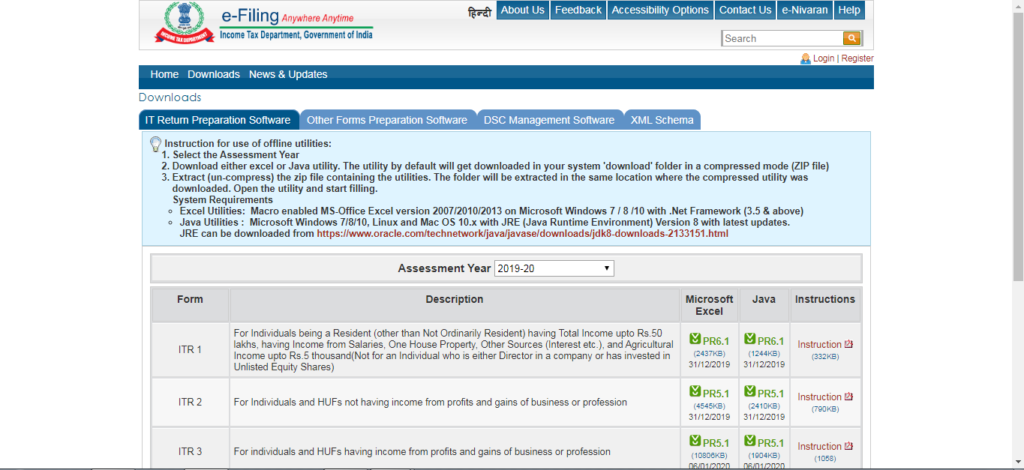
Step – 03 Select the right Assessment Year and download the offline based ITR utility software either in Excel or Java version as per your preference.
Step – 04 Once you have downloaded the utility form you can fill in the relevant details of your income and expenses. Once you have filled the right details and the number of deductions available to you, you can click on the ‘Validate’ button present at the right-hand side to see if all the required information is filled.
Step – 05 Once you have validated the information, you can then click on the ‘Calculate Tax’ button. The utility file will calculate the tax and showcase your liability.
Step – 06 After you have calculated your taxability you can click the ‘Generate XML’ button to convert the file into an XML file format. Save the XML file on your device.
Step – 07 Click on the Income Tax Portal website and log in your credentials. If you are a new user you can register yourself on the said link. If you are a registered user you can simply login therein as showcased in the screenshot.
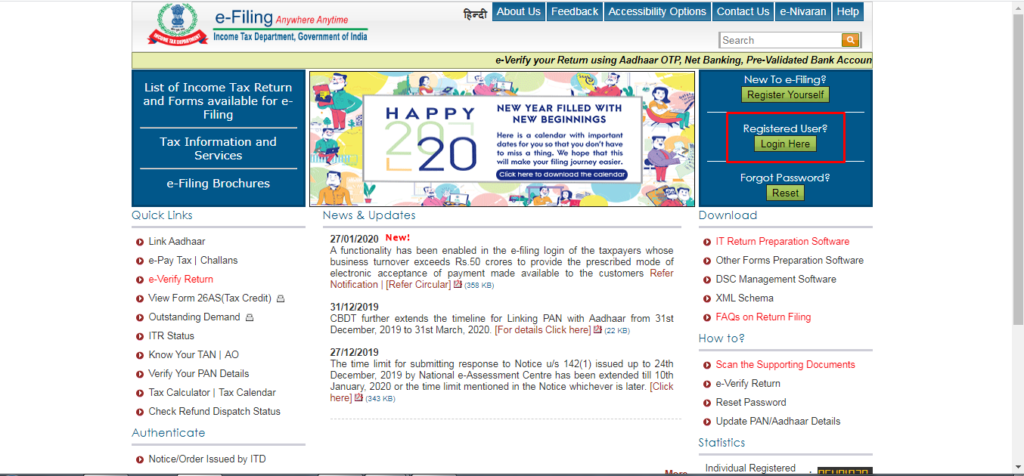
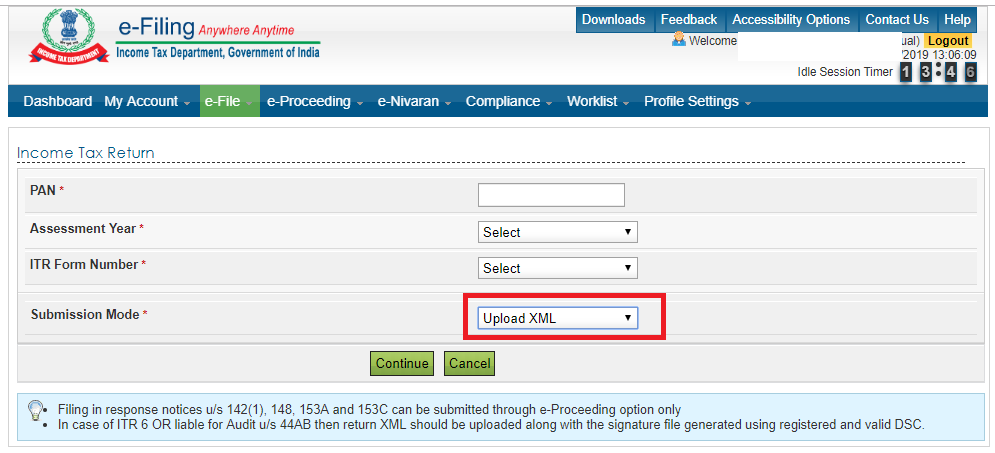
Step – 08 Once you have login your details you can proceed to click on the e-File section where a drop-down box will showcase Income Tax Return.
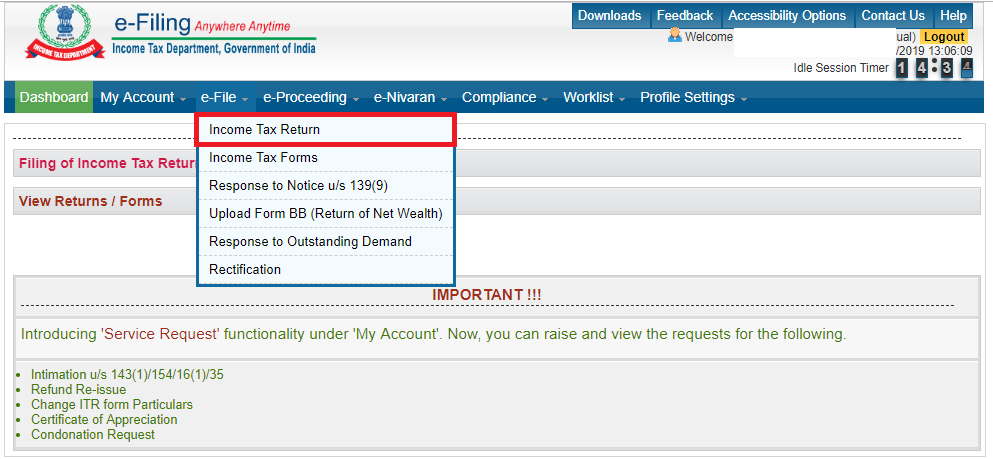
Step – 09 There as visible in the screenshot down below. You can insert your PAN number, Assessment Year, ITR Form No as required. Then click on the ‘Upload XML’ button where you should upload the XML file that you have previously filled and saved. You can choose from the available verification modes like Aadhaar OTP or Electronic Verification Code.